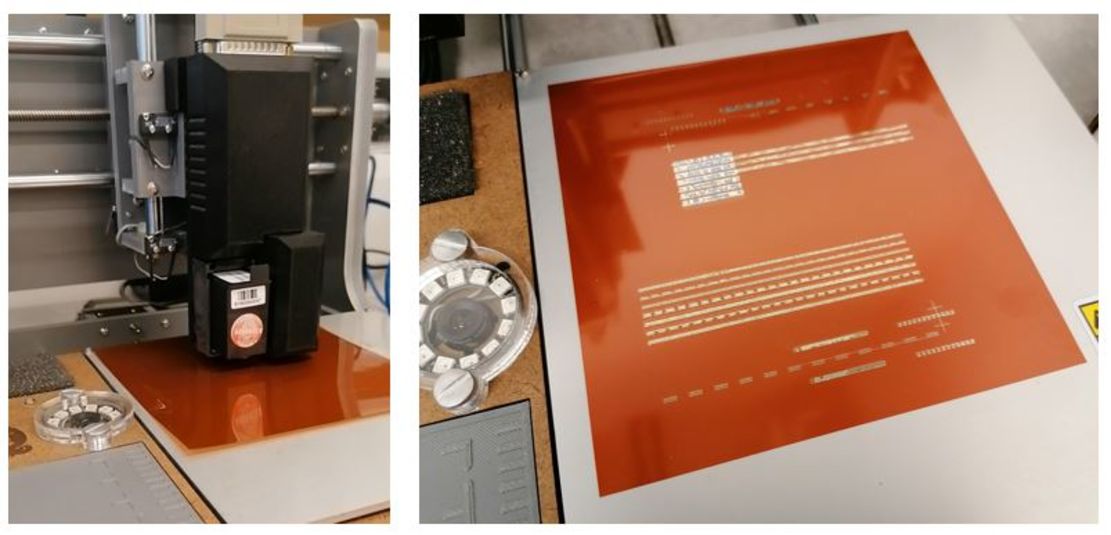
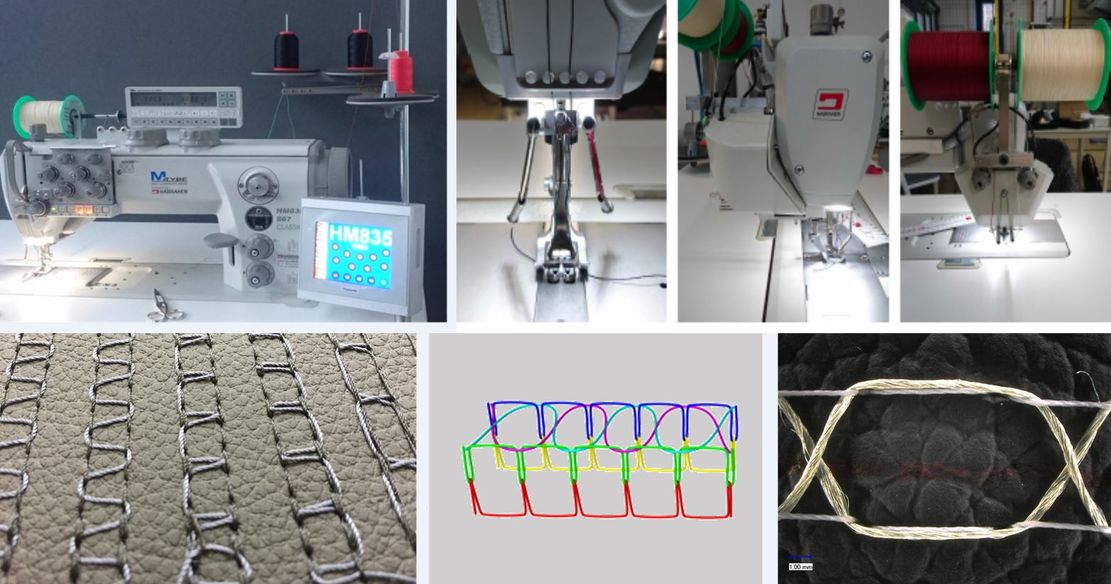
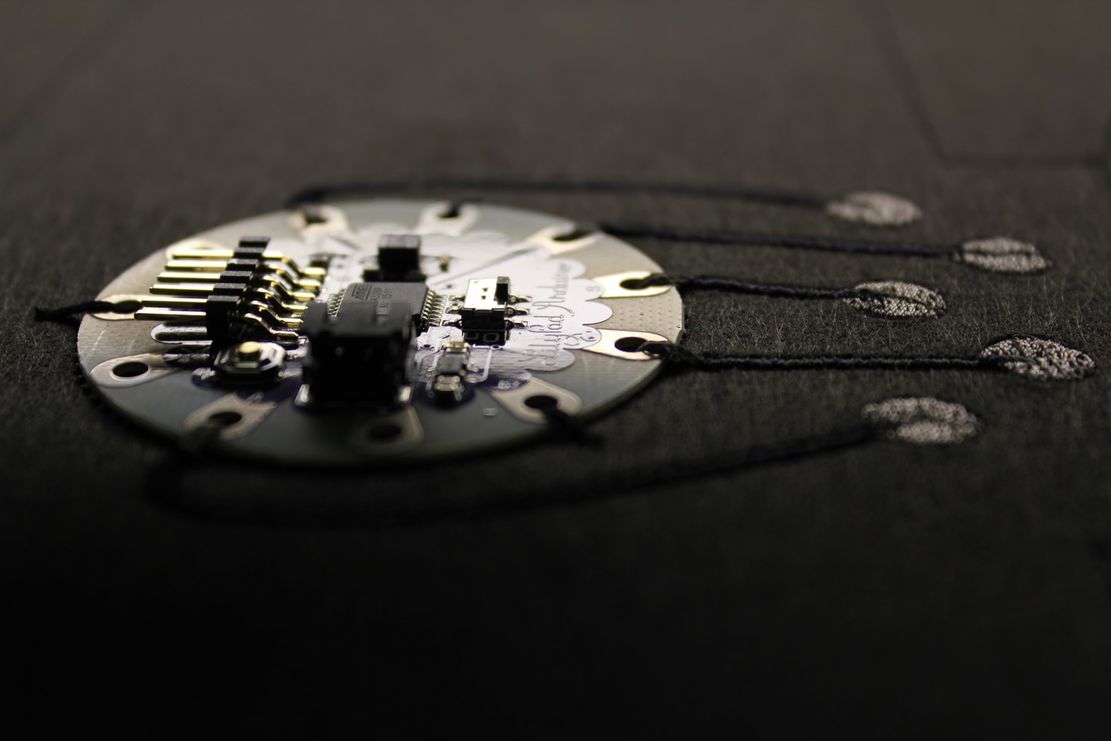
The multifunctional embroidery machine type SGVA of the company ZSK Stickmaschinen GmbH is a special machine, which has three different technical embroidery heads for different embroidery processes.
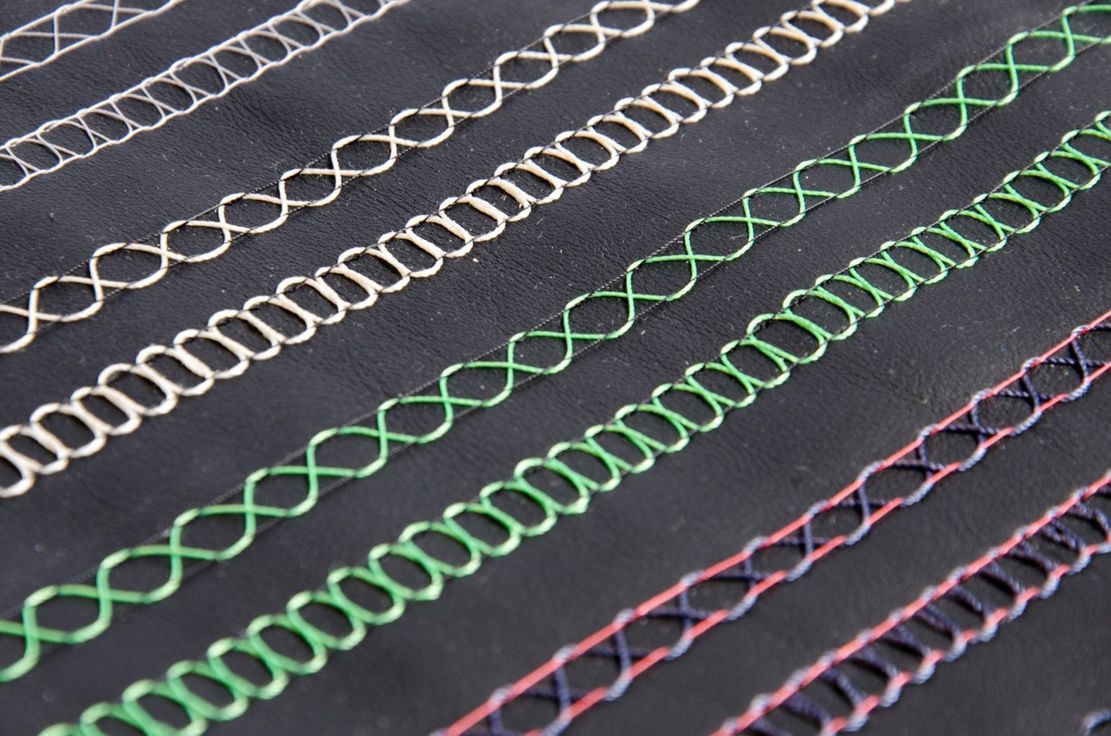
The F-head is a standard embroidery head with nine needles. This head has the technique of double-lock stitch embroidery and additionally enables embroidery applications such as sequin appliqué, drill embroidery, double-roll cord embroidery, as well as loop, cap and ribbon embroidery.
The K-head embroidery processes, the moss stitch and chain stitch, are single-thread systems. Here, the embroidery base is penetrated with a hook needle and the thread material fed from below is conveyed in a loop through the embroidery base to the upper side.
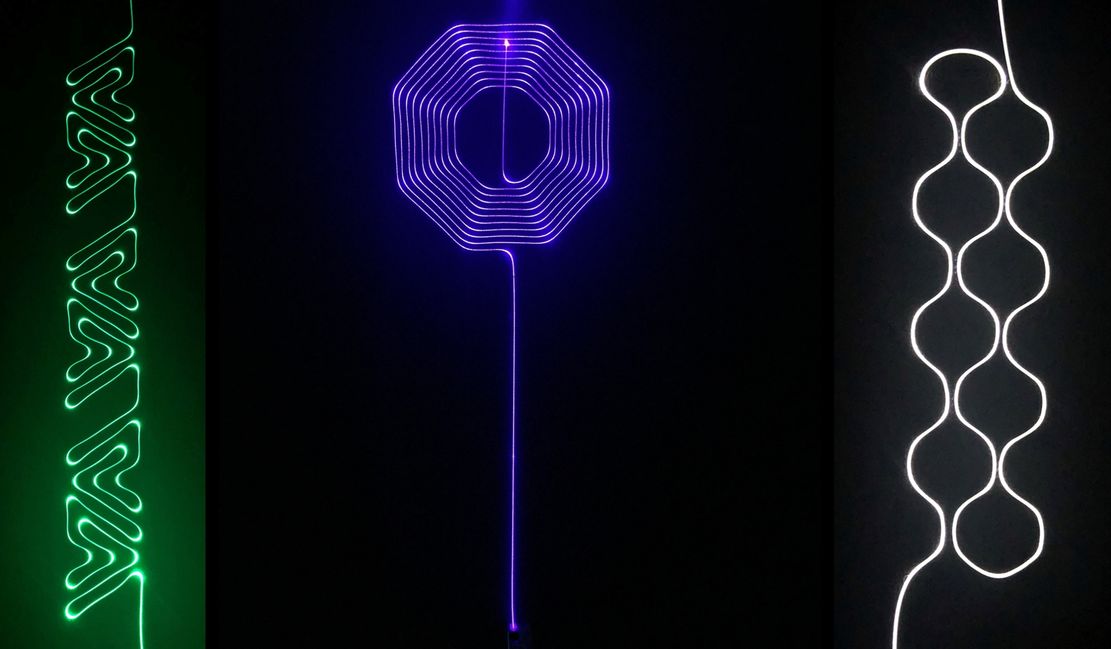
The W-head embroidery process is based on a three-thread system with upper and lower threads and a laying medium. The laying process is subdivided into three main technologies: Tailored Fibre Placement (TFP), Tailored Wire Placement (TWP) and Tailored Tube Placement (TTP).